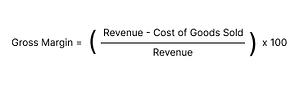Price
Distribution channels
Cross selling
Customer centric
Price elasticity
Sales index
Pricing AI
Understanding the gross margin concept is essential for retailers aiming to make informed pricing decisions. It represents the percentage of revenue remaining after covering the cost of goods sold (COGS). For any company, especially in retail, optimizing this metric can significantly impact overall profitability. In this article, we will delve into the details of what gross margin is, why it’s important, how it’s calculated, and how retailers can leverage it to develop robust pricing strategies. By mastering this metric, businesses can not only boost their profit but also enhance their market position. Want to master the language of pricing? We break down all the important concepts here. Gross margin is an important concept to master, especially in retail as it measures the profitability of products sold, guiding pricing and cost management to ensure long-term financial health. It directly impacts a retailer’s ability to cover operational expenses and generate sustainable profits. Gross margin is a financial metric that shows the percentage of sales revenue that exceeds the direct cost of producing the goods or services sold by a company. It reflects the portion of sales available to cover operating expenses and ultimately generate a profit. In simple terms, it’s the difference between revenue and the cost of goods sold (COGS), expressed as a percentage of total revenue. The gross margin helps businesses determine how efficiently they are managing their cost structure relative to their pricing strategy. For retailers, maintaining a healthy gross profit margin is crucial because it directly influences their ability to cover operating costs, invest in growth, and ensure profitability. Retailers need to balance their cost of goods and pricing strategies to maximize the gross margin. For example, increasing prices while keeping costs low will naturally boost the gross profit. Conversely, if costs rise without corresponding price adjustments, the gross margin will shrink, affecting the overall profit potential. Understanding gross margin is more than just knowing a number; it offers insights into how well a company can manage its operations, pricing, and future growth. Here’s why it’s essential: The gross margin is a critical measure of business efficiency, reflecting how well a retailer manages its direct costs relative to the revenue generated. A higher gross profit margin shows that a company can efficiently convert sales into profit. This allows retailers to: The gross margin also acts as an indicator of a retailer’s growth potential. If a business consistently achieves a healthy gross profit, it can reinvest in marketing, technology, or expansion. This reinvestment helps the company grow and maintain a competitive edge in the marketplace. On the other hand, a declining gross margin may signal issues with pricing strategies, supply chain management, or operational inefficiencies. Retailers must carefully monitor their gross profit margin to ensure long-term growth. Effective pricing strategies are designed to achieve the objective of increasing gross margin. The challenge for retailers is to strike the right balance between setting competitive prices and ensuring profitability. By focusing on implementing dynamic pricing strategies based on consumer behaviour, retailers can : A well thought-out pricing strategy enables companies to maintain a healthy gross margin while continuing to attract customers. At PricingHUB we offer tools to help our users optimise the pricing of their product catalogue according to their specific objectives, whether this involves improving gross margin, maximising profits or increasing sales volume. Meet one of our pricing experts The formula is straightforward: For example, if a retailer generates $1,000 in sales and the cost of goods sold is $600, the gross profit would be $400, and the gross margin would be: This formula helps retailers evaluate their pricing strategies by showing the percentage of sales revenue left after deducting the cost of goods. A higher gross profit margin means that the company retains more revenue from each sale, which can be reinvested into the business or used to cover operating expenses. For retailers, it’s essential to: If it decreases, it may signal the need for cost control or a pricing review. Monitoring this metric regularly ensures that retailers can adapt their strategies to maintain a strong profit margin. Retailers can further enhance their gross margin by leveraging technology such as PricingHUB’s machine learning tools. These pricing optimisation tools help retailers: By using advanced machine learning, retailers can optimize their gross margin while staying competitive in a fast-changing market. This technology provides actionable insights, ensuring that businesses can make data-driven pricing decisions to maximize profit. Gross margin is a crucial indicator of profitability and directly influences retail pricing strategies. By understanding their gross margin, retailers can determine how much they can afford to discount their products while maintaining profitability. It helps set competitive yet sustainable prices that ensure long-term financial health. Gross margin influences product pricing by helping retailers determine how much markup can be added to the cost of goods sold (COGS) to ensure a reasonable profit. Retailers need to balance costs, market demand, and competitive pricing to set a price that meets both consumer expectations and profitability goals. Several factors can affect gross margin, including production costs, pricing strategy, consumer demand, seasonality, and market conditions. Operational efficiency, like supply chain management and cost control, also plays a significant role in improving gross margin in retail businesses. Businesses can improve their gross margin ratio by reducing costs, increasing sales prices, and optimizing inventory management. Strategies like price optimization, product bundling, and offering premium products with higher profit margins can significantly boost a retailer’s gross margin. Gross margin is a key metric in financial forecasting as it helps businesses estimate their profitability and plan for future investments. By knowing the gross margin, retailers can create more accurate budgets and forecast how pricing adjustments, product changes, and market fluctuations will affect their bottom line. Discover all our pricing glossary articles Calculating a margin Omnichannel Relative price Rencontrez un de nos experts Pricing Everything You Need to Know About Gross Margin
What Is Gross Margin?
Definition
For instance, if a retailer has $1,000 in sales and a COGS of $600, their gross profit is $400, and their gross margin would be 40%. The higher it is, the more revenue a company retains from its sales, which is a key indicator of business health. How Does It Work?
Why Is Gross Margin Important to Understand?
Measuring Business Efficiency
Growth Potential Indicator
Helps Develop Pricing Strategies
– segment their offer according to consumer behaviour
– offer differentiated and adapted prices
– optimise their margins Gross Profit Margin Calculation
Discover the benefits of Machine Learning in our Pricing strategies
Formula
How to Understand the Results?
Optimize Your Gross Margin Using PricingHUB Machine Learning
Want to learn more about PricingHUB’s solution ? Request a demo Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Back margin
Front margin
Gross margin
Sales margin
Net margin
MSRP
Price bundling
Selling price
Psychological price
Price image
Safety stock
Brand rate
Up selling
Yield management
Dynamic pricing Évaluez le potentiel de l’élasticité prix sur votre business